4
March 2012
Introduction to JSF
Lecture Notes
![]()



I.Why JSF?
► JSF is view layer of Java EE standard
o Included with every Java EE server
o Open standard with multiple implementations
► JSF enforces the design principles of the JSP Model 2 architecture
► evolved from highly successful Struts framework
o Form Beans (“backing beans”) for every JSP page
► Performed validation and conversion
o Action objects for invoking model and navigation logic
► component-based framework
o components support encapsulation, extensibility, modularity, maintainability
o Pre-fabricated and custom components
o Event-driven components
► “Swing for server side apps”
o Every JSF tag has a corresponding Java component
► Framework phases based on recursing through the component tree
► Component tag versus component class
► E.g., h:inputText or h:selectOneRadio tags versus UIInput class
o Built-in and custom verification and validation of inputs
o
Ajax support
II.What is JSF?
► basic ingredients of a JSF app
o JSF pages
o (managed) beans
o [config file – faces.config.xml]
o web.xml DD
1. Basic ingredients of a
JSF application include JSF pages for the view (the known), the back end domain
logic and data (knower or underlying intelligence), and the JSF framework and FacesServlet and managed beans as the controller to
connect the view and model. Science of
Consciousness: The daily experience of pure awareness, the knower, is a best practice
for successful action.
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html">
<h:body>
<h:form>
<h3>Please enter your name and password.</h3>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Name:</td>
<td><h:inputText value="#{user.name}"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password:</td>
<td><h:inputSecret value="#{user.password}"/></td>
</tr>
</table>
<p><h:commandButton value="Login" action="welcome"/></p>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>
► p17-18 the main elements of a JSF page
o xhtml extension on pages,
o JSF tag libraries
o bean getters called for rendering page, setters called when page is submitted
§ note #{ … } EL syntax
o h:body, h:form, h:inputText, h:commandButton
o action attribute of commandButton specifies navigation rules
§ convention over configuration
@Named("user")
@SessionScoped
public class UserBean implements Serializable {
private String name;
private String password;
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String newValue) { name = newValue; }
public String getPassword() { return password; }
public void setPassword(String newValue) { password = newValue; }
}
► container managed Javabeans
o annotations and convention versus xml configuration files
o dependency injection
<servlet>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>javax.faces.webapp.FacesServlet</servlet-class>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>Faces Servlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/faces/*</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
► p19,20 web.xml maps urls to the faces servlet
o don’t write servlets anymore
o FacesServlet part of framework
► inspect the demo steps
o http://www.cs.mum.edu/courses/cs545/lectures/FaceletsLogin.htm
o How does the web.xml file differ from the one above?
o How does the login page differ from the one above?
o How does the managed bean differ?
2. JSF pages are like JSP pages that include special
tag libraries for interacting with the JSF framework. The JSF libraries provide all of the common
GUI components. EL expressions are
directly bound to the fields of business beans.
Science of Consciousness: Just like JSF pages allow us to write web apps with less
effort, the daily experience of pure awareness allows us to perform any
activity with less effort.
III.How Does JSF Work?
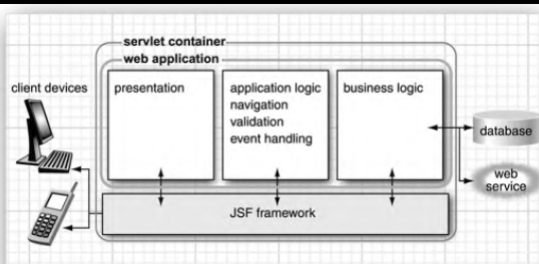
► JSF framework is MVC controller between view and model p24
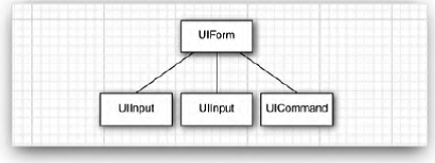
► JSF component tree is fundamental feature of framework
o framework walks tree to encode/generate/render markup p27-29
o framework walks tree to decode inputs for each component
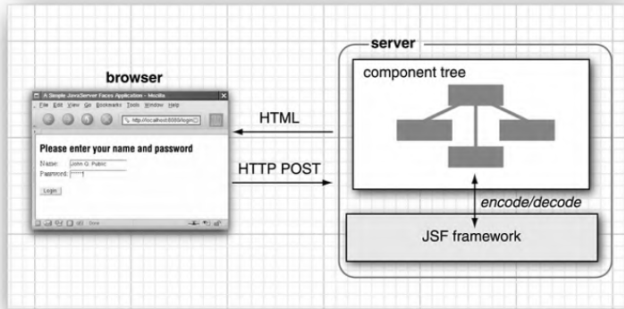
component.decode()
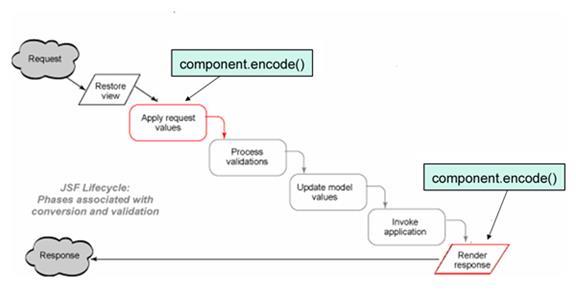
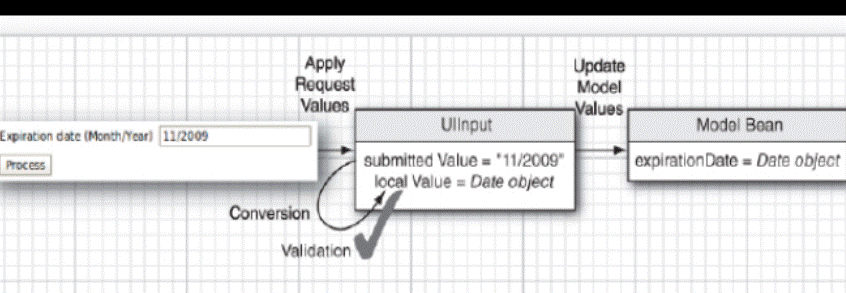
► p30 Phases of the JSF lifecycle
o Restore view – create/retrieve component tree
o Apply request values – assign request parameters to components
§ processDecodes() on UIViewRoot and ValueHolder components
o Process validations – ValueHolder components perform conversion and validation
o Update model values – UIInput components update model with validated inputs via processUpdates() and updateModel()
o Invoke application – ActionSource component executes business logic of model
o Render response – encodeXX() on components to generate markup
3. The JSF lifecycle includes phases for rebuilding
the component tree, getting input string parameters and saving them in the
component tree, data conversion and validation, updating the model, executing
business logic and then encoding the results in an appropriate JSF page and
response. Science of Consciousness: With
JSF all of these best practices are followed automatically. When we act from quiet levels of awareness we
automatically follow the best practices of nature.
► ajax version of demo—get source from corejsf source
o ajax tag,
o id’s on components
o and attributes
§ execute components get processed but not displayed
§
render components rendered but not processed
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml"
xmlns:h="http://java.sun.com/jsf/html"
xmlns:f="http://java.sun.com/jsf/core">
<h:body>
<h:form prependId="false">
<h3>Please enter your name and password.</h3>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Name:</td>
<td><h:inputText value="#{user.name}" id="name"/></td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>Password:</td>
<td><h:inputSecret value="#{user.password}" id="password"/></td>
</tr>
</table>
<p><h:commandButton value="Login">
<f:ajax execute="name password" render="out"/>
</h:commandButton></p>
<h3><h:outputText id="out" value="#{user.greeting}"/></h3>
</h:form>
</h:body>
</html>